

SECTION A
[40 marks]
Answer all the questions in this section.
All questions carry equal marks.
(1) (a) A man bought a car for \$8,000.00 and later sold it at a profit of 15%. He spent \$4,550.00 out of the amount received and invested the rest at 7% per annum simple interest. Calculate the interest earned in 4 years.
[5 marks]
Step 1: Calculate the selling price.
\[ \text{Selling Price} = \text{Cost Price} + \text{Profit} \]
\[ = 8,000 + (15\% \times 8,000) \]
\[ = 8,000 + \frac{15}{100} \times 8,000 \]
\[ = 8,000 + 1,200 \]
\[ = 9,200 \]
Step 2: Calculate the invested amount.
\[ \text{Invested Amount} = \text{Selling Price} - \text{Amount Spent} \]
\[ = 9,200 - 4,550 \]
\[ = 4,650 \]
Step 3: Use the simple interest formula.
\[ \text{Simple Interest} = \frac{P \times R \times T}{100} \]
\[ P = 4,650, R = 7\%, T = 4 \text{ years} \]
\[ \text{Interest} = \frac{4,650 \times 7 \times 4}{100} \]
\[ = \frac{130,200}{100} \]
\[ = 1,302 \]
Final Answer: The interest earned in 4 years is \$1,302.00.
(1). (b) Given that \( \log(3x - 1) + \log 2 = 2\log y \), find \( x \) in terms of \( y \).
[5 marks]
Step 1: Use the logarithmic property: \( \log a + \log b = \log (a \cdot b) \).
\[ \log(3x - 1) + \log 2 = \log [2(3x - 1)] \]
Step 2: Rewrite the right-hand side using the logarithmic exponent rule.
\[ \log [2(3x - 1)] = 2\log y \]
Step 3: Remove the logarithms by rewriting the equation in exponential form.
\[ 2(3x - 1) = y^2 \]
Step 4: Solve for \( x \).
\[ 3x - 1 = \frac{y^2}{2} \]
\[ 3x = \frac{y^2}{2} + 1 \]
\[ x = \frac{y^2 + 2}{6} \]
Final Answer: \( x = \frac{y^2 + 2}{6} \).
(2)
The cost of two chairs and three tables for an office is 1,800.00. After a month, the cost of each chair and each table increased by 20%. The office again bought 6 chairs and 2 tables at 4,800.00. Calculate the new cost of a chair and a table.
[10 marks]
Step 1: Let the original cost of a chair be x and a table be y.
From the first purchase:
\[ 2x + 3y = 1800 \quad \text{(Equation 1)} \]
Step 2: After the 20% increase:
The new cost of a chair = 1.2x, the new cost of a table = 1.2y
From the second purchase:
\[ 6(1.2x) + 2(1.2y) = 4800 \]
\[ 7.2x + 2.4y = 4800 \quad \text{(Equation 2)} \]
Step 3: Solve the two equations:
Multiply Equation 1 by 2.4: \[ 4.8x + 7.2y = 4320 \] Subtract:
\[ (7.2x + 2.4y) - (4.8x + 7.2y) = 480 \]
\[ 2.4x - 4.8y = 480 \quad \] \[\Rightarrow \quad x - 2y = 200 \] Substitute into Equation 1: \[ 2(200 + 2y) + 3y = 1800 \] \[ 400 + 4y + 3y = 1800 \quad \Rightarrow \] \[\quad 7y = 1400 \quad \] \[ \Rightarrow \quad y = 200 \] \[ x = 200 + 2(200) = 600 \]New chair cost: 1.2 × 600 = 720.00
New table cost: 1.2 × 200 = 240.00
(3)
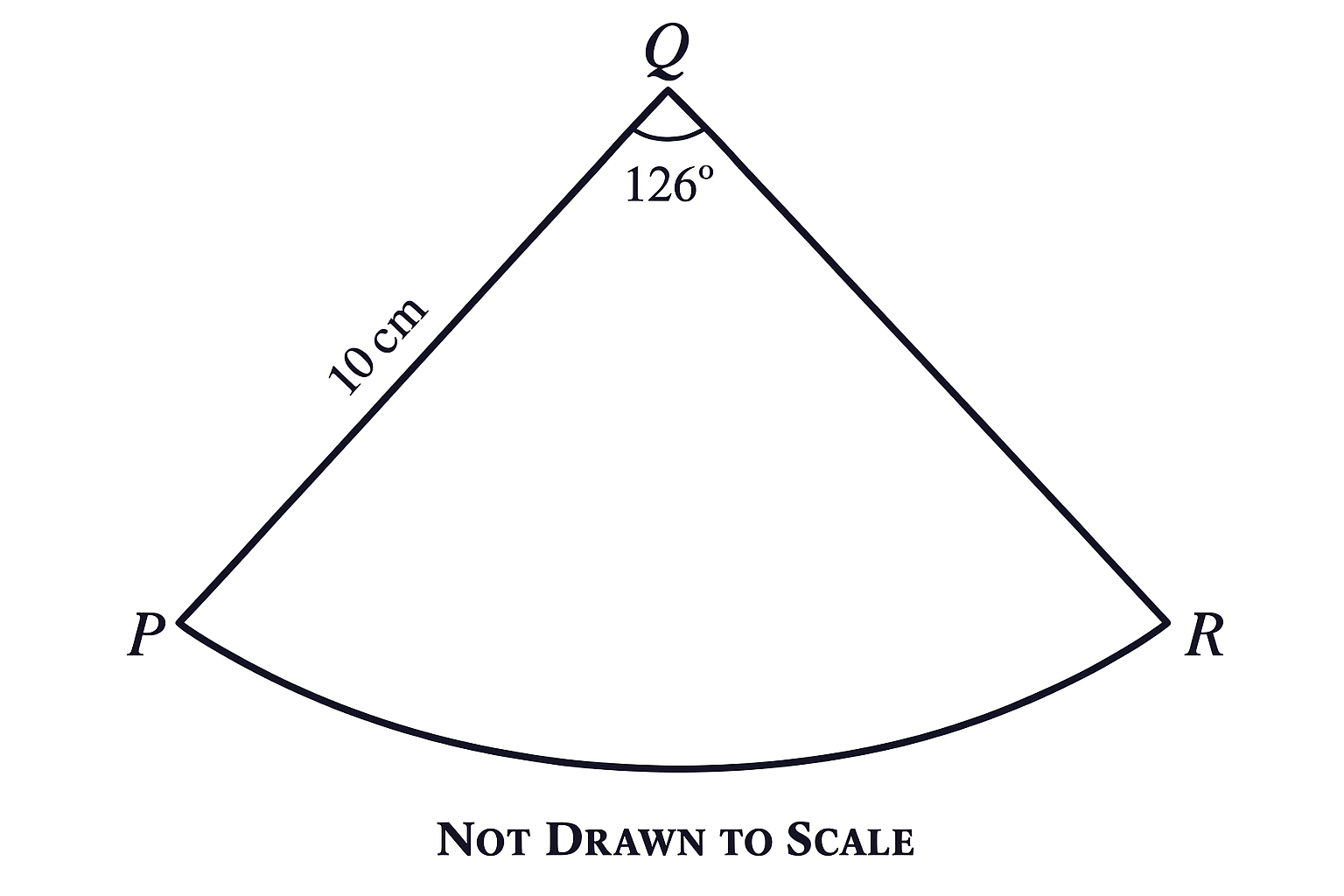
Step 1: Calculate arc length of the sector.
\[ \text{Arc length} = \frac{\theta}{360^\circ} \times 2 \pi r \] \[= \frac{126}{360} \times 2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 10 \]
\[ = \frac{7}{20} \times \frac{440}{7} = 22 \, \text{cm} \]
Step 2: Arc length becomes the circumference of the cone’s base.
\[ 2 \pi r_{\text{base}} = 22 \quad \Rightarrow \] \[ \quad r_{\text{base}} = \frac{22}{2 \times \frac{22}{7}} \] \[= \frac{22 \times 7}{44} = 3.5 \, \text{cm} \]
Step 3: Surface area of the cone.
The surface area is the lateral area of the cone (no base).
\[ \text{Surface Area} = \pi r_{\text{base}} l \] \[= \frac{22}{7} \times 3.5 \times 10 = 110 \, \text{cm}^2 \]
Final Answer: The surface area is 110 cm².
Step 1: Find the height using Pythagoras' Theorem.
\[ h = \sqrt{l^2 - r_{\text{base}}^2} \] \[= \sqrt{10^2 - 3.5^2} \] \[= \sqrt{100 - 12.25} \] \[= \sqrt{87.75} \approx 9.37 \, \text{cm} \]
Step 2: Calculate the volume.
\[ V = \frac{1}{3} \pi r_{\text{base}}^2 h \] \[= \frac{1}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times (3.5)^2 \times 9.37 \]
\[ = \frac{1}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times 12.25 \times 9.37 \] \[ \approx \frac{1}{3} \times 38.5 \times 9.37 \] \[ \approx \frac{1}{3} \times 360.745 \] \[\approx 120.25 \, \text{cm}^3 \]
Final Answer: The volume of the cone is approximately 120.25 cm³.
(4) The sum of the interior angles of two regular polygons is \( 2520^\circ \). If the number of sides of one of the polygons is 3 less than twice the number of sides of the other, find the number of sides of each of the polygons.
[5 marks]
Step 1: Use the sum of interior angles formula:
\[ S = (n - 2) \times 180 \]
Let the number of sides of the first polygon be \( n \), and the second polygon be \( 2n - 3 \).
From the given sum:
\[ (n - 2) \times 180 + ((2n - 3) - 2) \times 180 = 2520 \]
Step 2: Expand the equation:
\[ 180(n - 2) + 180(2n - 5) = 2520 \]
\[ 180n - 360 + 360n - 900 = 2520 \]
\[ 540n - 1260 = 2520 \]
Step 3: Solve for \( n \):
\[ 540n = 3780 \]
\[ n = \frac{3780}{540} = 7 \]
Step 4: Find the number of sides of the second polygon:
\[ 2n - 3 = 2(7) - 3 = 11 \]
Final Answer: The polygons have 7 sides and 11 sides, respectively.
(5) The scores of 15 students in a quiz competition are:
2, 6, 4, 7, 6, 8, 9, 5, 3, 5, 4, 2, 8, 7, 6.
(a) Calculate the mean of the scores.
(b) If a score is chosen at random, find the probability that it is:
(i) an even number;
(ii) at least 7.
[10 marks]
The mean is given by:
\[ \text{Mean} = \frac{\sum \text{Scores}}{\text{Total Count}} \]
\[ = \frac{2 + 6 + 4 + 7 + 6 + 8 + 9 + 5 + 3 + 5 + 4 + 2 + 8 + 7 + 6}{15} \]
\[ = \frac{82}{15} = 5.47 \]
Final Answer: The mean of the scores is 5.47.
List the even numbers in the set: 2, 6, 4, 6, 8, 4, 2, 8, 6.
Number of even numbers = 9.
\[ P(\text{even}) = \frac{9}{15} = \frac{3}{5} \]
Final Answer: \( P(\text{even}) = \frac{3}{5} \).
List the scores that are at least 7: 7, 8, 9, 7, 8.
Number of scores at least 7 = 5.
\[ P(\text{at least } 7) = \frac{5}{15} = \frac{1}{3} \]
Final Answer: \( P(\text{at least } 7) = \frac{1}{3} \).
SECTION B
[60 marks]
Answer five questions only from this section.
All questions carry equal marks.
(6)
The second, fourth and sixth terms of a Geometric Progression (G.P) are \( (2x - 4) \), \( (13x + 4) \) and \( (122x - 4) \) respectively. Find the:
(a) value of x;
(b) common ratio;
(c) first term.
[10 marks]
Step 1: Relationship in a G.P.
In a G.P., the ratio of consecutive terms is constant.
Let the first term be \( a \) and the common ratio be \( r \).
Second term: \( ar = 2x - 4 \)
Fourth term: \( ar^3 = 13x + 4 \)
Sixth term: \( ar^5 = 122x - 4 \)
Step 2: Form ratios.
\[ \frac{ar^3}{ar} = r^2 = \frac{13x + 4}{2x - 4} \] \[ \frac{ar^5}{ar^3} = r^2 = \frac{122x - 4}{13x + 4} \]
Step 3: Equate both expressions for \( r^2 \).
\[ \frac{13x + 4}{2x - 4} = \frac{122x - 4}{13x + 4} \]
Step 4: Cross-multiply.
\[ (13x + 4)^2 = (2x - 4)(122x - 4) \]
Step 5: Expand both sides.
\[ (169x^2 + 104x + 16) \] \[= (244x^2 - 8x - 488x + 16) \] \[ 169x^2 + 104x + 16 \] \[= 244x^2 - 496x + 16 \]
Step 6: Bring all terms to the left.
\[ 169x^2 + 104x + 16 - 244x^2 + 496x - 16 = 0 \]
\[ -75x^2 + 600x = 0 \] \[ -75x(x - 8) = 0 \]
Step 7: Solve for x.
\[
x = 0 \quad \text{or} \quad x = 8
\]
x = 0 is not meaningful in this context, so:
Final Answer: \( x = 8 \)
Step 1: Substitute \( x = 8 \) into second and fourth terms.
Second term: \( 2(8) - 4 = 12 \)
Fourth term: \( 13(8) + 4 = 108 \)
Step 2: Calculate common ratio \( r \).
\[ r^2 = \frac{108}{12} = 9 \quad \Rightarrow \quad r = 3 \]
Final Answer: The common ratio is 3.
Step 1: Use the second term formula.
\[ ar = 12 \quad \Rightarrow \] \[\quad a \times 3 = 12 \quad \Rightarrow \quad a = 4 \]
Final Answer: The first term is 4.
(7) Bala owns a hairdressing salon. He buys a pack of 60 bottles of shampoo from a warehouse for \$240.00 and sells a bottle for \$5.50.
(a) Calculate the percentage profit on each bottle of shampoo sold.
(b) If Bala sells 45 bottles at \$5.50 each and the rest at a 20% discount, calculate the total profit made on the 60 bottles.
[10 marks]
Step 1: Calculate the cost per bottle.
\[ \text{Cost per bottle} = \frac{\text{Total cost}}{\text{Number of bottles}} \]
\[ = \frac{240}{60} = 4.00 \]
Step 2: Find the profit per bottle.
\[ \text{Profit per bottle} = \text{Selling price} - \text{Cost price} \]
\[ = 5.50 - 4.00 = 1.50 \]
Step 3: Calculate the percentage profit.
\[ \text{Percentage Profit} = \frac{\text{Profit per bottle}}{\text{Cost price}} \times 100 \]
\[ = \frac{1.50}{4.00} \times 100 \]
\[ = 37.5\% \]
Final Answer: The percentage profit on each bottle is 37.5%.
Step 1: Find revenue from 45 bottles sold at full price.
\[ \text{Revenue} = 45 \times 5.50 = 247.50 \]
Step 2: Find revenue from 15 discounted bottles.
Discounted price per bottle:
\[ \text{Discounted price} = 5.50 \times (1 - 0.20) \]
\[ = 5.50 \times 0.80 = 4.40 \]
\[ \text{Revenue from discounted bottles} \] \[= 15 \times 4.40 = 66.00 \]
Step 3: Find total revenue.
\[ \text{Total Revenue} = 247.50 + 66.00 = 313.50 \]
Step 4: Find total profit.
\[ \text{Total Profit} = \text{Total Revenue} - \text{Total Cost} \]
\[ = 313.50 - 240.00 \]
\[ = 73.50 \]
Final Answer: The total profit made on the 60 bottles is \$73.50.
(8)
The data represent the ordered marks scored by 10 applicants in an interview:
3, 4, 2x, 5, (x + 4), (2x² − 1), (5x − 2), 8, 9 and 10.
(a) Given that the median mark is \(6 \frac{1}{2}\), find the:
(i) value of x;
(ii) mean mark.
(b) If the pass mark for the interview is 8, what percentage of the applicants passed?
[10 marks]
Step 1: Identify the middle terms.
Since there are 10 values, the median is the average of the 5th and 6th terms.
The 5th term is \( x + 4 \) and the 6th term is \( 2x^2 - 1 \).
Median: \[ \frac{(x + 4) + (2x^2 - 1)}{2} = 6.5 \]
Step 2: Solve for x.
\[ \frac{x + 4 + 2x^2 - 1}{2} = 6.5 \] \[ \frac{2x^2 + x + 3}{2} = 6.5 \] \[ 2x^2 + x + 3 = 13 \] \[ 2x^2 + x - 10 = 0 \]
Step 3: Solve the quadratic equation.
\[ (2x - 4)(x + 2.5) = 0 \] \[ x = 2 \quad \text{or} \quad x = -2.5 \]
Since the values must make sense in the ordered data, we accept x = 2.
Final Answer: x = 2.
Step 1: Substitute x = 2 into all variable terms.
The scores become: 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 8, 9, 10.
Step 2: Calculate the total sum.
\[ \text{Sum} = 3 + 4 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 8 + 9 + 10 = 64 \]
Step 3: Calculate the mean.
\[ \text{Mean} = \frac{64}{10} = 6.4 \]
Final Answer: The mean mark is 6.4.
Step 1: Identify the scores that are ≥ 8.
Pass marks: 8, 8, 9, 10 (4 students)
Step 2: Calculate the percentage.
\[ \text{Percentage Passed} = \frac{4}{10} \times 100\% \] \[= 40\% \]
Final Answer: 40% of the applicants passed the interview.
(9)
A man of height 1.62 m stood at a point, P, on a horizontal ground. He observed a stationary object, K, in the air at an angle of elevation of 32°. He moved 32 m directly towards the object to a point, Q, and observed the object at an angle of elevation of 42°.
(a) Illustrate the information in a diagram.
(b) Calculate, correct to the nearest whole number, the perpendicular distance from K to the ground.
[10 marks]
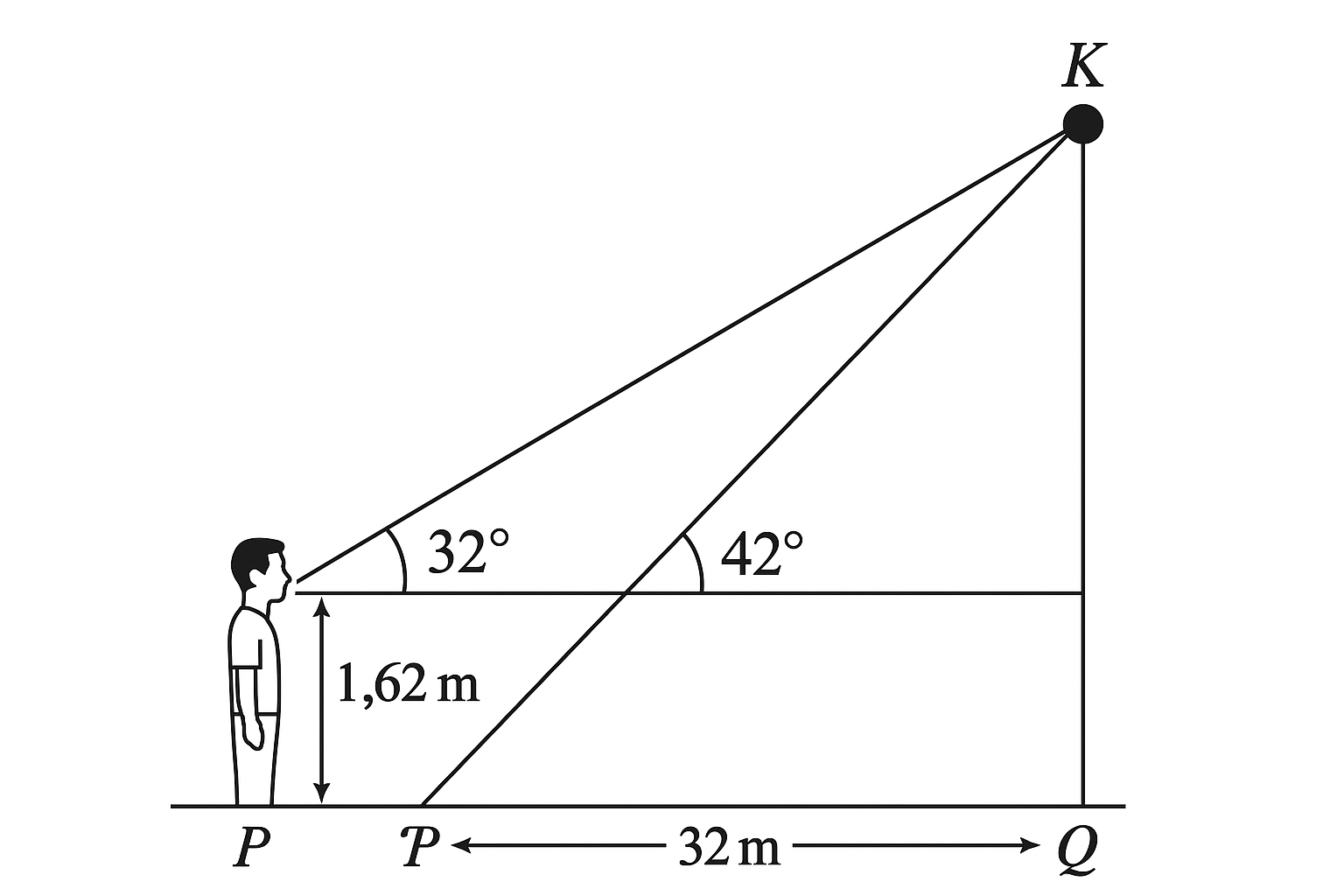
Step 1: Define variables and set up two right-angled triangles.
At Point P:
\[ \tan 32^\circ = \frac{h - 1.62}{x} \] \[ h - 1.62 = x \times \tan 32^\circ \quad \] \[\Rightarrow \quad h = x \times \tan 32^\circ + 1.62 \]
At Point Q:
Distance to the object is now \( x - 32 \) m. \[ \tan 42^\circ = \frac{h - 1.62}{x - 32} \] \[ h - 1.62 = (x - 32) \times \tan 42^\circ \quad \]
\[ \quad h = (x - 32) \times \tan 42^\circ + 1.62 \]
Step 2: Set both expressions for h equal.
\[ x \times \tan 32^\circ + 1.62 = (x - 32) \times \tan 42^\circ + 1.62 \]
\[ x \times \tan 32^\circ = (x - 32) \times \tan 42^\circ \]
\[ x \times \tan 32^\circ = x \times \tan 42^\circ - 32 \times \tan 42^\circ \]
\[ x ( \tan 32^\circ - \tan 42^\circ ) = -32 \times \tan 42^\circ \]
\[ x = \frac{ -32 \times \tan 42^\circ }{ \tan 32^\circ - \tan 42^\circ } \]
Step 3: Calculate the values.
\[ \tan 32^\circ \approx 0.6249 \quad \] \[\text{and} \quad \tan 42^\circ \approx 0.9004 \] \[ x = \frac{ -32 \times 0.9004 }{ 0.6249 - 0.9004 } \] \[= \frac{ -28.8128 }{ -0.2755 } \approx 104.6 \, \text{m} \]
Step 4: Find h.
\[ h = 104.6 \times 0.6249 + 1.62 \] \[\approx 65.42 + 1.62 \] \[\approx 67.04 \, \text{m} \]
Final Answer: The perpendicular distance from K to the ground is 67 m (to the nearest whole number).
(10) (a)
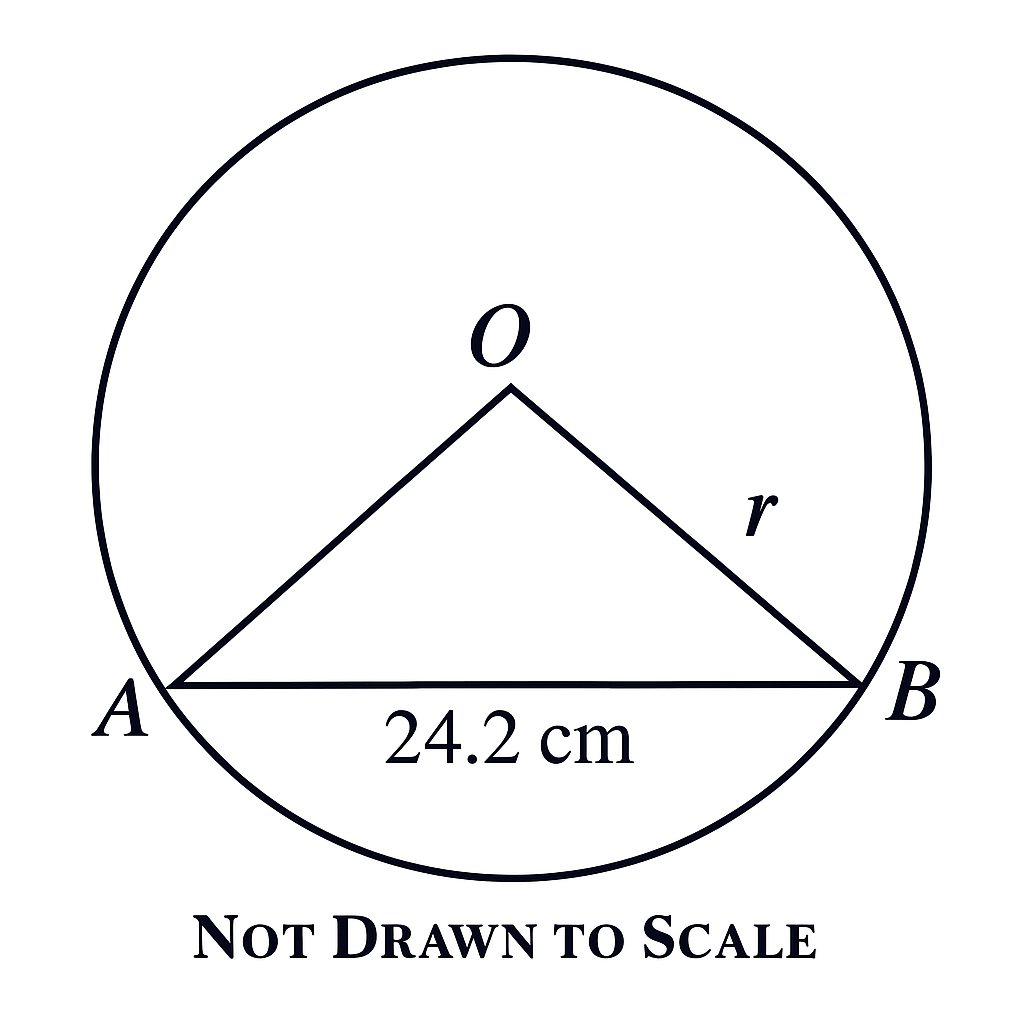
Step 1: Use the perimeter to find the radius.
\[ \text{Perimeter} = OA + OB + AB \] \[= 2r + 24.2 = 52.2 \] \[ 2r = 52.2 - 24.2 = 28 \quad \] \[\Rightarrow \quad r = 14 \, \text{cm} \]
Step 2: Use the cosine rule to find \( \angle AOB \).
\[ \cos(\angle AOB) = \frac{OA^2 + OB^2 - AB^2}{2 \cdot OA \cdot OB} \]
\[ = \frac{14^2 + 14^2 - 24.2^2}{2 \cdot 14 \cdot 14} \] \[ = \frac{392 - 585.64}{392} \] \[= \frac{-193.64}{392} \approx -0.493 \]
Step 3: Calculate the angle using inverse cosine:
\[ \angle AOB = \cos^{-1}(-0.493) \] \[\approx 118.5^\circ \Rightarrow \boxed{119^\circ} \]
Final Answer: \( \angle AOB \approx \boxed{119^\circ} \)
Step 1: Find the slope (gradient) of the line passing through (1, 4) and (3, 0).
\[ m = \frac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1} \] \[= \frac{0 - 4}{3 - 1} = \frac{-4}{2} = -2 \]
Step 2: Use point-slope form to find the equation.
\[ y - y_1 = m(x - x_1) \Rightarrow \] \[y - 4 = -2(x - 1) \] \[ y = -2x + 2 + 4 = -2x + 6 \]
Final Answer: The equation of the line is \( \boxed{y = -2x + 6} \)
(11) (a)
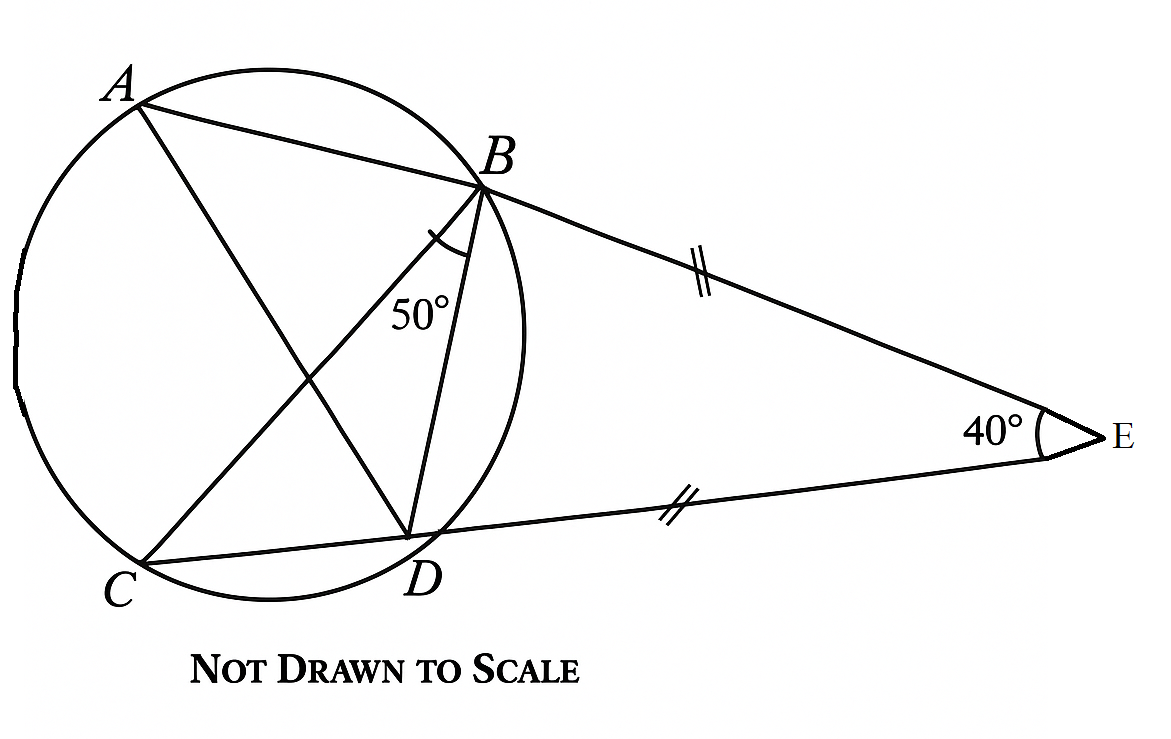
Step 1: Use triangle BED to find \( \angle EBD \).
Since \( BE = DE \), triangle \( BED \) is isosceles.
Therefore, \( \angle EBD = \angle EDB \)
\[ \angle EBD = \angle EDB \] \[ = \frac{180^\circ - 40^\circ}{2} = 70^\circ \]
Step 2: Find \( \angle DBC \) using angle subtraction.
\[ \angle DBC = \angle EBD - \angle CBD \] \[= 70^\circ - 50^\circ = 20^\circ \]
Step 3: Use the circle theorem:
\( \angle BAD \) is equal to \( \angle DBC \) because they subtend the same arc \( BD \).
So,
\[
\angle BAD = \angle DBC = \boxed{20^\circ}
\]
Final Answer: \( \angle BAD = \boxed{20^\circ} \)
(11) (b)
The length and width of a rectangle are in the ratio 5 : 2 respectively. If the perimeter of the rectangle is 70 cm, calculate the area.
[5 marks]
Step 1: Let the length = 5x and the width = 2x.
Step 2: Use the perimeter formula:
\[ P = 2(\text{length} + \text{width}) = 70 \] \[ 2(5x + 2x) = 70 \] \[ 2(7x) = 70 \Rightarrow \] \[14x = 70 \Rightarrow x = 5 \]
Step 3: Calculate actual length and width:
\[ \text{Length} = 5x = 5 \times 5 = 25 \, \text{cm} \] \[ \text{Width} = 2x = 2 \times 5 = 10 \, \text{cm} \]
Step 4: Calculate area:
\[ \text{Area} = \text{Length} \times \text{Width} \] \[= 25 \times 10 = 250 \, \text{cm}^2 \]
Final Answer: The area of the rectangle is 250 cm².
(12) (a)
A basket contains three types of fruits A, B, and C, all of the same size. The total number of fruits is 20 and the probability of selecting fruit C is \( \frac{3}{10} \). If the number of fruit B is 1 less than twice the number of fruit A, find the number of each type of fruit in the basket.
[5 marks]
Step 1: Use the probability of selecting fruit C.
\[ \text{P(C)} = \frac{3}{10} \Rightarrow \] \[\text{Number of C} = \frac{3}{10} \times 20 \] \[= 6 \]
Step 2: Let the number of fruit A be \( x \). Then fruit B is:
\[ \text{B} = 2x - 1 \]
Step 3: Total number of fruits:
\[ A + B + C = 20 \Rightarrow \] \[x + (2x - 1) + 6 = 20 \] \[ 3x + 5 = 20 \] \[ 3x = 15 \] \[ x = 5 \]
Step 4: Find each value:
\[ \text{A} = 5, \] \[\quad \text{B} = 2(5) - 1 = 9, \] \[\quad \text{C} = 6 \]
Final Answer: A = 5, B = 9, C = 6.
(12) (b)
Solve: \( 2\log_{10}x - \log_{10}9 = 4 \)
[5 marks]
Step 1: Use log rules to combine the terms.
\[ 2\log_{10}x - \log_{10}9 = 4 \] \[ \log_{10}(x^2) - \log_{10}(9) = 4 \] \[ \log_{10}\left(\frac{x^2}{9}\right) = 4 \]
Step 2: Rewrite in exponential form.
\[ \frac{x^2}{9} = 10^4 = 10000 \] \[ x^2 = 10000 \times 9 = 90000 \]
Step 3: Take square root of both sides.
\[ x = \sqrt{90000} = 300 \]
Final Answer: \( x = \mathbf{300} \)
(13) (a)
Copy and complete the table of values for \( y = 2x^2 - x - 4 \) for \( -3 \leq x \leq 3 \).
| x | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | -1 | 2 |
Given: \( y = 2x^2 - x - 4 \)
Step-by-step Computations:
\( x = -3 \):
\[
y = 2(-3)^2 - (-3) - 4 \] \[ = 18 + 3 - 4 \] \[= \mathbf{17}
\]
\( x = -2 \):
\[
y = 2(-2)^2 - (-2) - 4 \] \[= 8 + 2 - 4 \] \[= \mathbf{6}
\]
\( x = -1 \):
\[
y = 2(-1)^2 - (-1) - 4 \] \[= 2 + 1 - 4 \] \[= \mathbf{-1}
\]
\( x = 0 \):
\[
y = 2(0)^2 - 0 - 4 \] \[= \mathbf{-4}
\]
\( x = 1 \):
\[
y = 2(1)^2 - 1 - 4 \] \[= 2 - 1 - 4 \] \[= \mathbf{-3}
\]
\( x = 2 \):
\[
y = 2(2)^2 - 2 - 4 \] \[= 8 - 2 - 4 \] \[= \mathbf{2}
\]
\( x = 3 \):
\[
y = 2(3)^2 - 3 - 4 \] \[= 18 - 3 - 4 \] \[= \mathbf{11}
\]
Completed Table:
| x | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 17 | 6 | -1 | -4 | -3 | 2 | 11 |
Final Answer: All values computed and table completed accurately.
(13) (b)
Using a scale of 2 cm to 1 unit on the x-axis and 2 cm to 2 units on the y-axis, draw the graph of
\[
y = 2x^2 - x - 4 \quad \text{for} \] \[\quad -3 \leq x \leq 3.
\]
Step 1: Calculate \( y \) values for integer \( x \) from -3 to 3:
Step 2:ploted Graph:
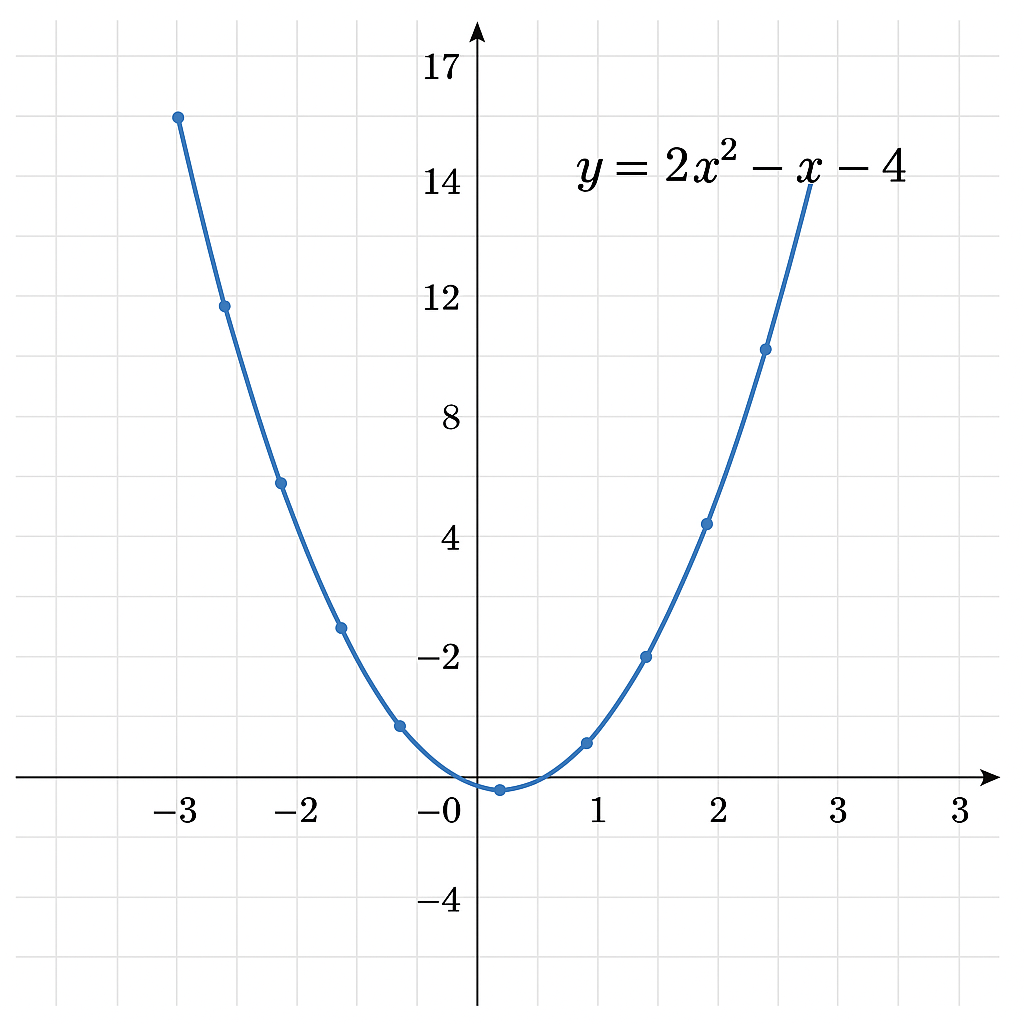
Final note: The graph is a parabola opening upwards with vertex near \(x = \frac{1}{4}\).

(13)(c) Use the graph to find the:
(i) Roots of the equation \( y = 2x^2 - x - 4 = 0 \)
(ii) Range of values of \( x \) for which \( y \) decreases as \( x \) increases.
(iii) Minimum point.
[15 marks]
(i) Roots of the equation:
The roots are the x-values where the curve intersects the x-axis.
From the graph, these roots are approximately:
\[ x \approx -1.5 \quad \text{and} \quad x \approx 1.5 \]
(ii) Range where y decreases as x increases:
The graph decreases for values of \( x \) less than the vertex.
This happens when:
\[ x < 0.25 \]
(iii) Minimum point:
The minimum point is the vertex of the parabola, which appears to be:
\[ (0.25, -4.125) \]
Final Summary:
Our Mission: To provide free, accessible, and comprehensive exam preparation resources for West African students preparing for their WASSCE and LJHSCE examinations.
StudyWASSCE was created in 2023 by an independent content creator who recognized a critical gap in accessible educational resources for West African students. After witnessing countless students struggle to find quality past examination papers and affordable study materials, I dedicated myself to building a comprehensive, completely free platform that would level the playing field for all students, regardless of their economic background.
As an independent educational content creator, I have invested countless hours researching, compiling, and organizing past examination papers from official sources. My commitment stems from a deep belief that every student deserves access to quality educational resources, regardless of their financial circumstances.
Unlike general educational platforms, StudyWASSCE specializes exclusively in:
StudyWASSCE operates on a sustainable model that keeps education free while ensuring quality:
Since launching, StudyWASSCE has:
As an independent creator, I am committed to:
We welcome partnerships with:
As the independent creator behind StudyWASSCE, I personally respond to:
Response Commitment: I personally review and respond to all messages within 48-72 hours.
Education transformed my life, and I believe it can transform the lives of every student who has access to quality resources. StudyWASSCE represents my personal commitment to ensuring that no student is left behind due to lack of access to study materials. Every hour I spend improving this platform is an investment in the future of West African education.
Thank You for Your Support! By using StudyWASSCE and viewing our advertisements, you help sustain this free educational resource. Your success is our success, and every student who passes their examinations using our materials validates our mission.
StudyWASSCE: Created by an independent educator, for students everywhere.
Empowering West African students through free, accessible education.
StudyWASSCE is an independent educational platform created to provide free access to past exam papers and study materials for WASSCE and LJHSCE examinations. We are committed to helping students succeed while maintaining transparency about our data practices.
To improve our service and comply with advertising requirements, we collect the following information:
We use collected information to:
Our site is supported by advertising to keep educational content free. We work with the following third-party services:
We do not sell or rent personal information. We may share data with:
Required for Site Access: By using StudyWASSCE, you consent to our data collection practices as described in this policy. This includes:
Your Options:
Note: Continued use of our platform indicates your ongoing consent to these practices.
We implement appropriate technical and organizational security measures to protect the information we collect. However, no internet transmission is completely secure, and we cannot guarantee absolute security.
Our site is designed for students of all ages. We do not knowingly collect personal information from children under 13 without parental consent. If you believe we have collected such information, please contact us immediately.
Our site is hosted and operated from servers that may be located in different countries. By using our site, you consent to the transfer of your information to these locations.
We may update this privacy policy periodically to reflect changes in our practices or legal requirements. We will post any changes on this page with an updated revision date. Continued use of our site after changes constitutes acceptance of the updated policy.
If you have any questions about this privacy policy or our data practices, please contact us via WhatsApp at +231-770450825, by email at davidlamine96@gmail.com, or through our Facebook page @Study For WASSCE.
Last Updated: January 15, 2025
Important Notice: By using StudyWASSCE, you agree to these Terms of Service and our Privacy Policy. This site uses cookies and displays advertisements to provide free educational content.
StudyWASSCE is an independent educational platform created and maintained by a dedicated content creator who has worked extensively to compile and organize past examination papers for WASSCE (West African Senior School Certificate Examination) and LJHSCE (Liberian Junior High School Certificate Examination). Our mission is to provide free access to quality educational resources for students preparing for these national examinations.
All examination papers, questions, and educational materials on this platform have been carefully curated from publicly available past examination papers. We provide:
By accessing, browsing, or using StudyWASSCE in any way, you acknowledge that you have read, understood, and agree to be bound by these Terms of Service and our Privacy Policy. If you do not agree to these terms, please discontinue use of our platform immediately.
StudyWASSCE provides completely free access to all educational content. You are not required to:
To maintain this free service, StudyWASSCE is supported by:
Required for Free Access: Advertisements are essential to maintaining our free educational service. By using StudyWASSCE, you consent to the display of advertisements throughout the platform.
Our advertising practices comply with Google AdSense policies:
Essential for Site Operation: StudyWASSCE uses cookies for:
By using our site, you consent to our use of cookies as described in our Privacy Policy.
StudyWASSCE grants you a limited, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use our content for personal educational purposes only. You may:
You may NOT:
While individual examination questions may be public domain, our compilation, organization, explanations, and presentation represent original work protected by intellectual property rights.
We use Google Analytics to collect anonymous usage data to improve our educational content and user experience. This includes:
We use this data to:
Users must:
StudyWASSCE is designed for students of all ages. Users under 13 should have parental consent before using our platform, particularly regarding cookie acceptance and data collection.
While we strive for accuracy in all educational content:
Important: StudyWASSCE is a study supplement and should not replace formal education, textbooks, or qualified instruction. Users should use our resources alongside official study materials and classroom learning.
We strive to maintain consistent platform availability, but cannot guarantee:
We reserve the right to:
We are committed to protecting user privacy while providing free educational services. Our data collection practices are detailed in our Privacy Policy and comply with:
Our platform integrates with reputable third-party services that have their own privacy policies:
StudyWASSCE is provided "as is" for educational purposes. We disclaim liability for:
In no event shall StudyWASSCE be liable for any indirect, incidental, special, or consequential damages arising from platform use, even if advised of the possibility of such damages.
Our advertising practices comply with:
We respect intellectual property rights and maintain compliance with copyright laws regarding educational fair use of examination materials.
We regularly update our platform with:
We reserve the right to modify these Terms of Service to:
Updated terms will be posted on this page with revision dates. Continued use after changes constitutes acceptance of updated terms.
These Terms of Service shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of the Republic of Liberia. Any disputes arising from these terms or platform use shall be subject to the jurisdiction of Liberian courts.
If any provision of these Terms of Service is found to be unenforceable or invalid, that provision shall be limited or eliminated to the minimum extent necessary so that the remaining terms remain in full force and effect.
These Terms of Service, together with our Privacy Policy, constitute the entire agreement between you and StudyWASSCE regarding platform use and supersede all prior agreements or understandings.
For questions about these Terms of Service, content issues, or platform feedback, please contact us through:
For Urgent Issues: Technical problems affecting site access, inappropriate advertisements, or content errors.
For Partnership Inquiries: Educational institutions, content contributors, or collaboration opportunities.
Thank you for using StudyWASSCE! Your use of our platform helps us continue providing free educational resources to students across West Africa. We appreciate your support through advertisement viewing and ethical use of our content.
© 2025 StudyWASSCE. All rights reserved.
Supporting West African education through free access to quality study materials.