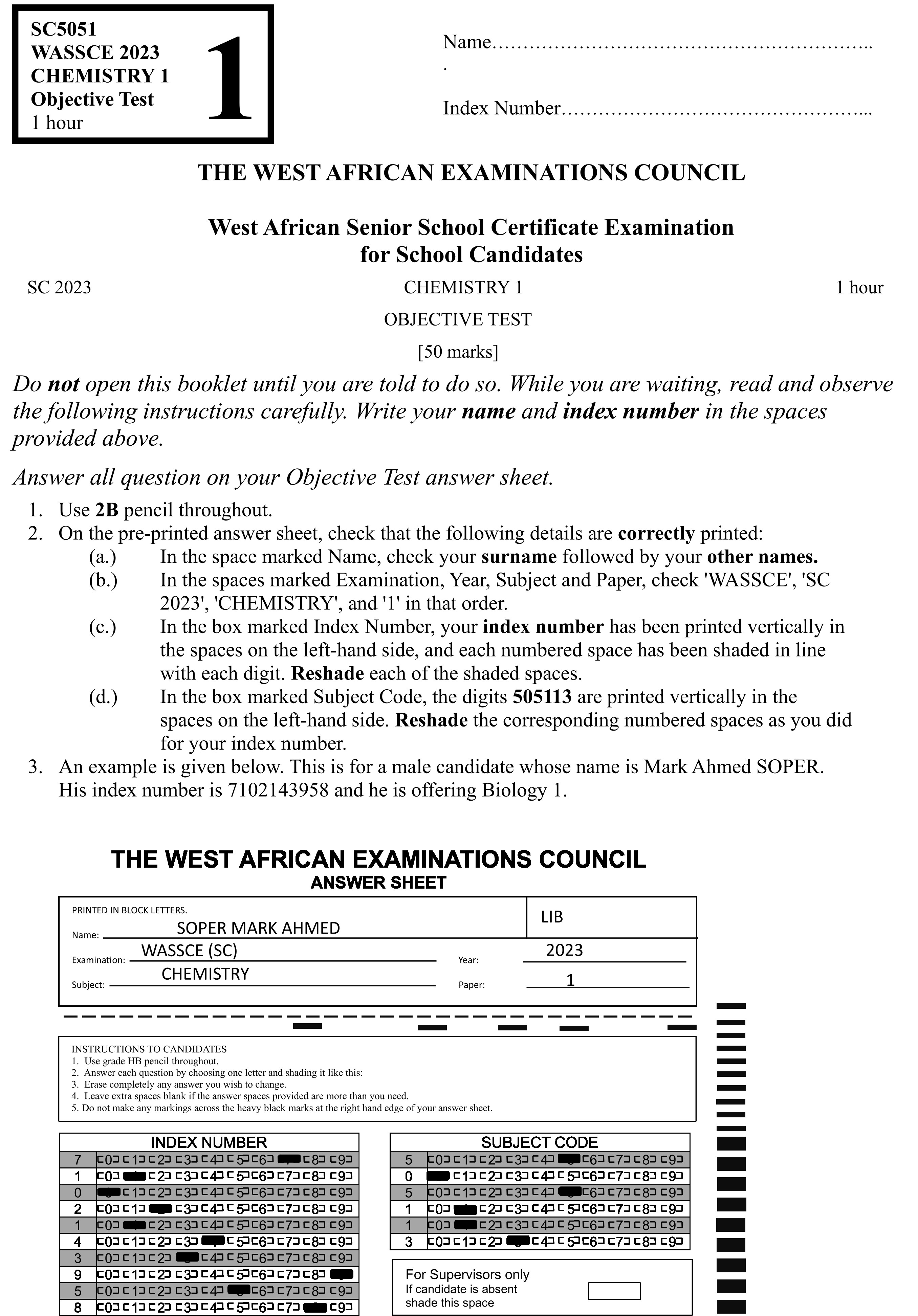

Answer all the questions
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct option for each question and shade in pencil on your answer sheet, the answer space which bears the same letter as the option you have chosen. Give only one answer to each question. An example is given below.
Which of the following elements reacts with water?
A. Carbon.
B. Sodium.
C. Sulphur.
D. Iodine.




The correct answer is Sodium which is lettered D and therefore answer space D would be shaded.
Think carefully before you shade the answer spaces; erase completely any answer(s) you wish to change.
Do all rough work on this question paper.
Now answer the following questions.
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D. Dalton's atomic theory
Dalton's atomic theory is about the nature of matter, stating that all matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. It is not explained by the kinetic theory of gases.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A. Methane
Methane (CH4) makes up most of natural gas (about 70–90%). It is the simplest hydrocarbon and the main fuel used for heating and electricity generation.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B. Involves decomposition
Thermal cracking is a process where large alkane molecules break down (decompose) into smaller hydrocarbons, such as alkanes and alkenes. It is used in petroleum refining to produce more useful products like gasoline and ethene.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C. Incomplete combustion of petrol
Carbon deposits form in exhaust pipes when petrol burns without enough oxygen. Instead of forming carbon dioxide, some carbon remains as soot, which builds up in the exhaust system.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B. 0.5
In CuCl₂, copper exists as Cu2+. This means 2 moles of electrons (2 Faradays) are needed to deposit 1 mole of copper. Therefore, passing 1 Faraday will deposit 0.5 moles of copper.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C. The cracking of hydrocarbons
Cracking breaks down large hydrocarbon molecules (such as long-chain alkanes) into smaller, more useful molecules like alkanes and alkenes. This is the main industrial method of producing alkenes.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C. Applied chemistry
Petrochemistry involves converting crude oil and natural gas into useful products such as plastics, fuels, and fertilizers. It is considered applied chemistry because it uses chemical principles for practical, industrial purposes.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A. Intermediates
Intermediates are formed during some steps of a reaction mechanism and then used up in later steps. They do not appear in the overall balanced equation because they are temporary species.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A. Pentane has five isomers
Pentane (C5H12) has three structural chain isomers (n-pentane, isopentane, and neopentane) and additional stereoisomers, making a total of five isomers. This makes option A correct.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B. Phenolphthalein
Phenolphthalein is best for titrating a weak acid like ethanoic acid with a strong base like sodium hydroxide. It changes color in the basic pH range, which accurately shows the endpoint of this titration.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C. Cu2+(aq) + 2e− → Cu(s)
In this reaction, copper ions gain two electrons to form solid copper. This gain of electrons is a reduction process.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B. 0.74 mol dm−3
Step-by-step:
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A. sodium trioxocarbonate (IV)
Sodium trioxocarbonate (IV), also called sodium carbonate, is crystalline but does not contain water of crystallization.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B. Neutral
Ethanoic acid (a weak acid) reacts with sodium hydroxide (a strong base) to form sodium acetate. The strong base neutralizes the weak acid, producing a neutral salt solution.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C. CH3COOC2H5 + H2O → CH3COO− + CH3CH2OH
The hydrolysis of an ester (alkanoate) breaks the ester bond using water, forming an alcohol and a carboxylate ion. In this case, ethyl ethanoate reacts with water to form acetate ions and ethanol.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D. Rate of reaction is proportional to the number of effective collisions
Collision theory states that particles must collide with sufficient energy and proper orientation to react. Only these "effective collisions" cause reactions. The more effective collisions there are, the faster the reaction rate.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A. React with the gas
Ammonia reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid and calcium chloride instead of being simply dried. This changes its composition, making them unsuitable drying agents.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B. Cl2 + 2NaF → 2NaCl + F2
Fluorine is more reactive than chlorine, so chlorine cannot displace fluorine from sodium fluoride. Therefore, this reaction is not possible.
Here's why the other answers are correct:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A. 5
Iron (Fe) has atomic number 26, with configuration [Ar] 3d6 4s2. For Fe3+, three electrons are removed (two from 4s, one from 3d), leaving 3d5. Each of the five 3d orbitals has one unpaired electron, so there are 5 unpaired electrons.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D. Electronegativity decreases
As you go down Group II, atoms get bigger because more shells are added. The outer electrons are farther from the nucleus and are more shielded, so the nucleus pulls them less strongly. This makes electronegativity decrease.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D. Sodium
Sodium has one outer electron in the 3s orbital, so it is an s-block element.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B. Electronegativity
Electronegativity is how strongly an atom pulls shared electrons in a bond. If two atoms have different electronegativity values, the bond will be uneven, making the molecule polar.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C. Open-mindedness
Open-mindedness is an attitude of a good scientist, but it is not one of the formal steps of the scientific method. The main steps are: observation, problem identification, hypothesis, experiment, data collection, and analysis.
Here's why the other answers are correct steps:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D. Electrons
Isoelectronic species are atoms or ions that have the same number of electrons. For example: O2−, F−, Na+, and Ne all have 10 electrons.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B. 65.50
To calculate the relative atomic mass:
So, the average relative atomic mass is 65.50.
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A. C₂H₆ and C₄H₁₀
C₂H₆ (ethane) and C₄H₁₀ (butane) are both alkanes. They belong to the same homologous series because they have the same general formula and the same functional group.
Members of a homologous series differ by a CH₂ unit.
Why others are wrong:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D. Flooding
Global warming causes the polar ice caps to melt. This makes sea levels rise, which increases the chance of flooding in low-lying coastal areas.
Why others are wrong:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B. Oxygen
According to Graham’s Law, gases with higher molar mass diffuse more slowly.
Since oxygen has the highest molar mass, it diffuses the slowest.
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D. Nitrogen
Air has an average molar mass of about 29 g/mol. Nitrogen (N₂) has a molar mass of 28 g/mol, so it is slightly lighter (less dense) than air.
Why others are wrong:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A. H₂SO₄(aq)
Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) is a strong acid and ionizes completely in water. Each molecule produces 2 H⁺ ions and 1 SO₄²⁻ ion. This gives a large number of ions in solution, so it conducts electricity the best.
Why others are wrong:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D. Cations are discharged
At the cathode, cations (positively charged ions) gain electrons. This process is called reduction, and it discharges them as neutral atoms or molecules.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C. 0.80 g
We use the formula: moles = concentration × volume.
Convert 100.0 cm3 to dm3: 100.0 cm3 = 0.100 dm3.
Now, moles of NaOH = 0.20 × 0.100 = 0.020 mol.
Mass = moles × molar mass = 0.020 × 40.0 = 0.80 g.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C. Polarity
When hydrogen bonds with a highly electronegative atom (like oxygen, fluorine, or nitrogen), the electrons are shared unequally. This causes polarity in the molecule.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A. Cl2
Cl2 has a non-polar covalent bond because both chlorine atoms have the same electronegativity, so the electrons are shared equally.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
| Element | Ionization energy (kJ mol-1 × 10-3) |
|---|---|
| W | 12.0 |
| X | 21.0 |
| Y | 106.0 |
| Z | 200.0 |
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C. W and X only
Elements with lower ionization energy lose electrons more easily, which makes them more reactive with chlorine. W (12.0) and X (21.0) have the lowest ionization energies, so they react most readily with chlorine.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D. 15
Vapour density is calculated using:
Vapour Density = Relative Molar Mass ÷ 2
So, 30 ÷ 2 = 15.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A. 198 kJ of energy is absorbed
A positive ∆H means the reaction is endothermic, so energy is absorbed from the surroundings.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D. Polymerization
The kinetic theory of matter is supported by physical processes that show particle motion, such as melting, diffusion, and evaporation.
Polymerization, on the other hand, is a chemical reaction where small molecules join to form larger ones. It does not provide evidence of particle motion in the same way.
Here's why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C. An alkaline gas
Concentrated tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid (H2SO4) is used to dry alkaline gases such as ammonia because it removes water without reacting much with the gas. Calcium oxide cannot be used because it is basic and would react with the alkaline gas instead of just drying it.
Here’s why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B. Metallic bonds
In metallic bonding, positive metal ions are packed in a structure and surrounded by free-moving electrons (a "sea of electrons"). This is why metals can conduct electricity and be bent without breaking.
Here’s why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C. It is a strong oxidizing agent
Dilute trioxonitrate (V) acid (HNO3) does not release hydrogen when reacting with metals because instead of forming hydrogen gas, it oxidizes the hydrogen into water or forms nitrogen oxides.
Here’s why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B. 0.0625
Molar mass of O3 = 3 × 16 = 48 g/mol.
Moles = mass ÷ molar mass = 3.0 ÷ 48 = 0.0625 mol.
Here’s why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B. Have vacant d-orbital
Copper(II) ions (Cu2+) can accept lone pairs of electrons because they have empty d-orbitals. This makes them able to form coordinate covalent bonds with ligands.
Here’s why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A. 400 cm3
Using the formula: Concentration = moles ÷ volume.
Volume = moles ÷ concentration = 0.100 ÷ 0.250 = 0.4 dm3 = 400 cm3.
Here’s why the other answers are incorrect:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C. The total kinetic energy of the gas is not affected by collision
In gases, molecules move freely and collide often. These collisions can change the energy of individual molecules, but the total kinetic energy of all the molecules stays the same as long as the temperature does not change. That means statement C is wrong, because collisions do affect how energy is shared.
Why the other options are correct:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D. HF, NH3, SiH4, CH4
HF has the highest boiling point because it forms very strong hydrogen bonds.
NH3 also makes hydrogen bonds, but they are weaker than those in HF, so its boiling point is lower than HF.
SiH4 and CH4 are nonpolar molecules, so they only have weak London forces, giving them much lower boiling points.
Order: HF > NH3 > SiH4 > CH4
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A. There is a large decrease in the volume of a solid metal when pressure is applied to it
Solids like metals are almost incompressible, so their volume does not change much under pressure. This makes statement A incorrect.
Why the other statements are correct:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A. 30
Vapour density is found by dividing the relative molecular mass (RMM) by 2.
For C2H4O2:
Total RMM = 24 + 4 + 32 = 60
Vapour density = 60 ÷ 2 = 30
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B. Crystallization
Crystallization separates salts when they have different solubility. The less soluble salt forms crystals first as the solution cools or the solvent evaporates.
Why the other options are wrong:
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C. Solvent extraction
Solvent extraction is used because iodine dissolves better in another solvent (like alcohol) than in tetrachloromethane. This makes it possible to pull out the iodine.
Why the other options are wrong:
Our Mission: To provide free, accessible, and comprehensive exam preparation resources for West African students preparing for their WASSCE and LJHSCE examinations.
StudyWASSCE was created in 2023 by an independent content creator who recognized a critical gap in accessible educational resources for West African students. After witnessing countless students struggle to find quality past examination papers and affordable study materials, I dedicated myself to building a comprehensive, completely free platform that would level the playing field for all students, regardless of their economic background.
As an independent educational content creator, I have invested countless hours researching, compiling, and organizing past examination papers from official sources. My commitment stems from a deep belief that every student deserves access to quality educational resources, regardless of their financial circumstances.
Unlike general educational platforms, StudyWASSCE specializes exclusively in:
StudyWASSCE operates on a sustainable model that keeps education free while ensuring quality:
Since launching, StudyWASSCE has:
As an independent creator, I am committed to:
We welcome partnerships with:
As the independent creator behind StudyWASSCE, I personally respond to:
Response Commitment: I personally review and respond to all messages within 48-72 hours.
Education transformed my life, and I believe it can transform the lives of every student who has access to quality resources. StudyWASSCE represents my personal commitment to ensuring that no student is left behind due to lack of access to study materials. Every hour I spend improving this platform is an investment in the future of West African education.
Thank You for Your Support! By using StudyWASSCE and viewing our advertisements, you help sustain this free educational resource. Your success is our success, and every student who passes their examinations using our materials validates our mission.
StudyWASSCE: Created by an independent educator, for students everywhere.
Empowering West African students through free, accessible education.
StudyWASSCE is an independent educational platform created to provide free access to past exam papers and study materials for WASSCE and LJHSCE examinations. We are committed to helping students succeed while maintaining transparency about our data practices.
To improve our service and comply with advertising requirements, we collect the following information:
We use collected information to:
Our site is supported by advertising to keep educational content free. We work with the following third-party services:
We do not sell or rent personal information. We may share data with:
Required for Site Access: By using StudyWASSCE, you consent to our data collection practices as described in this policy. This includes:
Your Options:
Note: Continued use of our platform indicates your ongoing consent to these practices.
We implement appropriate technical and organizational security measures to protect the information we collect. However, no internet transmission is completely secure, and we cannot guarantee absolute security.
Our site is designed for students of all ages. We do not knowingly collect personal information from children under 13 without parental consent. If you believe we have collected such information, please contact us immediately.
Our site is hosted and operated from servers that may be located in different countries. By using our site, you consent to the transfer of your information to these locations.
We may update this privacy policy periodically to reflect changes in our practices or legal requirements. We will post any changes on this page with an updated revision date. Continued use of our site after changes constitutes acceptance of the updated policy.
If you have any questions about this privacy policy or our data practices, please contact us via WhatsApp at +231-770450825, by email at davidlamine96@gmail.com, or through our Facebook page @Study For WASSCE.
Last Updated: January 15, 2025
Important Notice: By using StudyWASSCE, you agree to these Terms of Service and our Privacy Policy. This site uses cookies and displays advertisements to provide free educational content.
StudyWASSCE is an independent educational platform created and maintained by a dedicated content creator who has worked extensively to compile and organize past examination papers for WASSCE (West African Senior School Certificate Examination) and LJHSCE (Liberian Junior High School Certificate Examination). Our mission is to provide free access to quality educational resources for students preparing for these national examinations.
All examination papers, questions, and educational materials on this platform have been carefully curated from publicly available past examination papers. We provide:
By accessing, browsing, or using StudyWASSCE in any way, you acknowledge that you have read, understood, and agree to be bound by these Terms of Service and our Privacy Policy. If you do not agree to these terms, please discontinue use of our platform immediately.
StudyWASSCE provides completely free access to all educational content. You are not required to:
To maintain this free service, StudyWASSCE is supported by:
Required for Free Access: Advertisements are essential to maintaining our free educational service. By using StudyWASSCE, you consent to the display of advertisements throughout the platform.
Our advertising practices comply with Google AdSense policies:
Essential for Site Operation: StudyWASSCE uses cookies for:
By using our site, you consent to our use of cookies as described in our Privacy Policy.
StudyWASSCE grants you a limited, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use our content for personal educational purposes only. You may:
You may NOT:
While individual examination questions may be public domain, our compilation, organization, explanations, and presentation represent original work protected by intellectual property rights.
We use Google Analytics to collect anonymous usage data to improve our educational content and user experience. This includes:
We use this data to:
Users must:
StudyWASSCE is designed for students of all ages. Users under 13 should have parental consent before using our platform, particularly regarding cookie acceptance and data collection.
While we strive for accuracy in all educational content:
Important: StudyWASSCE is a study supplement and should not replace formal education, textbooks, or qualified instruction. Users should use our resources alongside official study materials and classroom learning.
We strive to maintain consistent platform availability, but cannot guarantee:
We reserve the right to:
We are committed to protecting user privacy while providing free educational services. Our data collection practices are detailed in our Privacy Policy and comply with:
Our platform integrates with reputable third-party services that have their own privacy policies:
StudyWASSCE is provided "as is" for educational purposes. We disclaim liability for:
In no event shall StudyWASSCE be liable for any indirect, incidental, special, or consequential damages arising from platform use, even if advised of the possibility of such damages.
Our advertising practices comply with:
We respect intellectual property rights and maintain compliance with copyright laws regarding educational fair use of examination materials.
We regularly update our platform with:
We reserve the right to modify these Terms of Service to:
Updated terms will be posted on this page with revision dates. Continued use after changes constitutes acceptance of updated terms.
These Terms of Service shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of the Republic of Liberia. Any disputes arising from these terms or platform use shall be subject to the jurisdiction of Liberian courts.
If any provision of these Terms of Service is found to be unenforceable or invalid, that provision shall be limited or eliminated to the minimum extent necessary so that the remaining terms remain in full force and effect.
These Terms of Service, together with our Privacy Policy, constitute the entire agreement between you and StudyWASSCE regarding platform use and supersede all prior agreements or understandings.
For questions about these Terms of Service, content issues, or platform feedback, please contact us through:
For Urgent Issues: Technical problems affecting site access, inappropriate advertisements, or content errors.
For Partnership Inquiries: Educational institutions, content contributors, or collaboration opportunities.
Thank you for using StudyWASSCE! Your use of our platform helps us continue providing free educational resources to students across West Africa. We appreciate your support through advertisement viewing and ethical use of our content.
© 2025 StudyWASSCE. All rights reserved.
Supporting West African education through free access to quality study materials.