
PAPER 2
[80 marks]
Answer four questions in all. One question only from Section A and any three questions from section B.
You are reminded of the importance of clarity of expression and orderly presentation of relevant materials.
All questions carry equal marks.
SECTION A
Answer One question only from this section.
1. The production possibility curve (PPC) in Figure 1 below shows different combinations of clothes and shoes that can be produced by a country. Study the graph and answer the questions that follow.
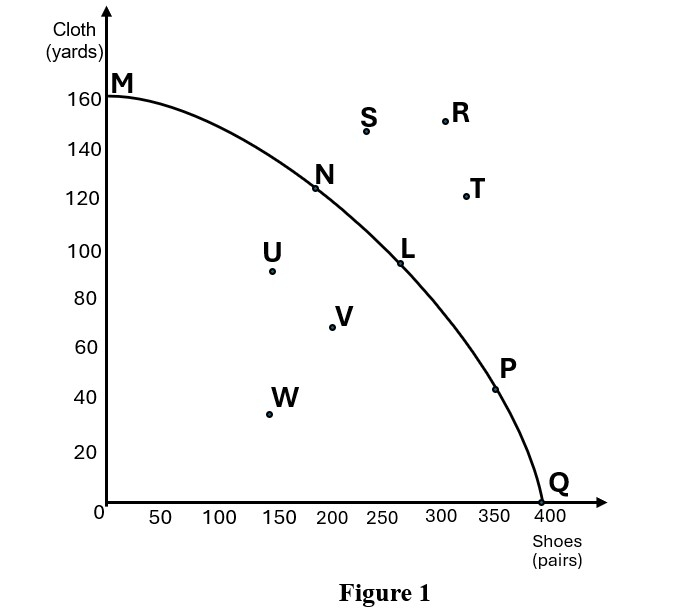
(1) (a) State three efficient combinations of clothes and shoes that can be produced from the PPC in Figure 1.
[6 marks]
(1) (b) Identify two points that are unattainable in production. Give a reason for your answer.
[3 marks]
(1) (c) Identify two points that are inefficient in production. Give a reason for your answer.
[3 marks]
(1) (d) What is the opportunity cost of shifting from point L to P?
[2 marks]
(1) (e)
(i) State two things the country can do in order to produce at point R?
[4 marks]
(ii) If there is a parallel shift of the curve to point R, what does it signify in the economy?
[2 marks]
2. Table 1 below shows the relationship between the input of labour employed and the output of wheat produced on 3 hectares of land. 1 kg of wheat is sold for $1.00 and the wage rate per labour is $5.00. Study the table and answer the questions that follow.
| LAND (HECTARE) | INPUT OF LABOUR | QUANTITY OF WHEAT (KG) |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 | 10 |
| 3 | 2 | 25 |
| 3 | 3 | 30 |
| 3 | 4 | 32 |
(2) (a) Calculate the average product of labour when the labour input employed is:
(i) 1
[2 marks]
(ii) 3
[2 marks]
(2) (b) Calculate the marginal product of labour at all levels of labour input employed.
[8 marks]
(2) (c) At what level(s) of labour input employed is the farmer experiencing:
(i) Increasing returns;
[2 marks]
(ii) Diminishing returns?
[2 marks]
(2) (d) From your answers in (c)(ii) above, give a reason for the diminishing marginal product of labour.
[4 marks]
(3) (a) Define elasticity of demand.
[2 marks]
(3) (b) (i) Explain the effect of price elasticity of demand on:
Government policy of currency devaluation as it affects imports.
[6 marks]
(3) (b) (ii) Explain the effect of price elasticity of demand on:
The total revenue of a monopolist.
[6 marks]
(3) (b) (iii) Explain the effect of price elasticity of demand on:
The total revenue of a government from an indirect tax.
[6 marks]
(4) (a) Define minimum wage.
[2 marks]
(4) (b) Identify any two factors that can encourage an employer to offer a higher wage rate.
[6 marks]
(4) (c) With the aid of a diagram, explain how fixing a minimum wage can create unemployment.
[12 marks]
(5) (a) Define cash crop production.
[2 marks]
(5) (b) Explain any three contributions of cash crop production to the economy of a country.
[9 marks]
(5) (c) Identify any three causes of unstable incomes of cash crop farmers.
[9 marks]
(6) (a) Explain the following concepts:
(i) Per capita income;
[3 marks]
(ii) Standard of living.
[3 marks]
(6) (b) Describe the relationship between per capita income and standard of living.
[5 marks]
(6) (c) Highlight any three problems involved in calculating national income using the income approach.
[9 marks]
(7) (a) With an example, define public expenditure.
[3 marks]
(7) (b) Explain how public expenditure can be managed in order to:
(i) curb inflation;
[4 marks]
(ii) reduce unemployment.
[4 marks]
(7) (c) Outline any three sources of funds for financing public expenditure.
[9 marks]
(8) (a) Differentiate between the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank.
[4 marks]
(8) (b) Outline four contributions of the World Bank to the economic development of a country.
[16 marks]